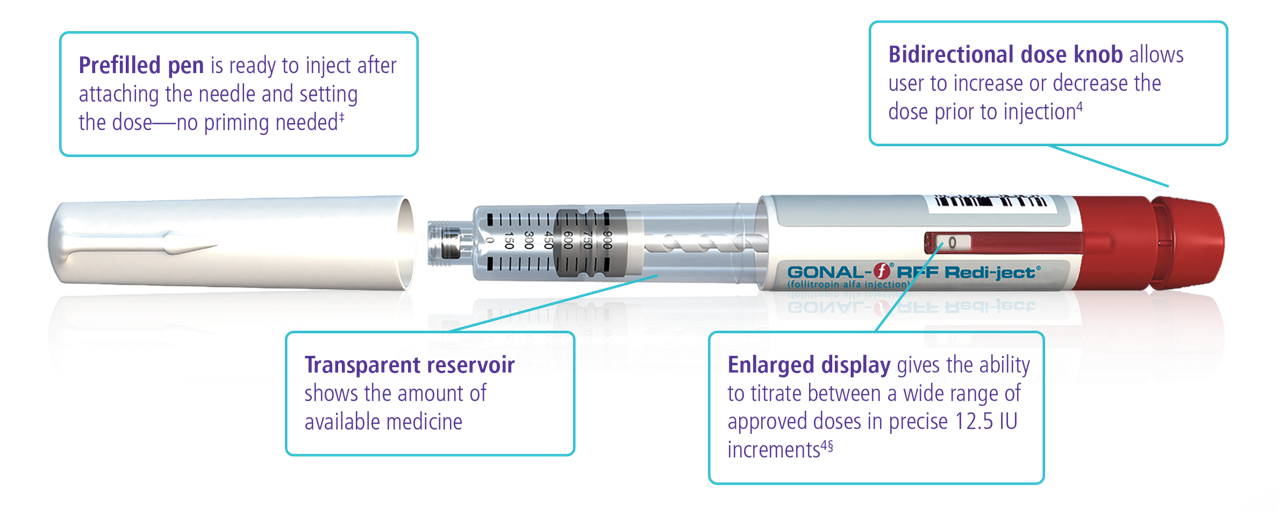
Designed to induce follicle development
Induction of ovulation and pregnancy in oligo-anovulatory women in whom the cause of infertility is functional and not due to primary ovarian failure.
Prior to initiation of treatment with GONAL-f® RFF* Redi-ject®:
- Perform a complete gynecologic and endocrinologic evaluation
- Exclude primary ovarian failure
- Exclude the possibility of pregnancy
- Demonstrate tubal patency
- Evaluate the fertility status of the male partner
Development of multiple follicles in ovulatory women as part of an assisted reproductive technology (ART) cycle.
Prior to initiation of treatment with GONAL-f RFF® Redi-ject®:
- Perform a complete gynecologic and endocrinologic evaluation, and diagnose the cause of infertility
- Exclude the possibility of pregnancy
- Evaluate the fertility status of the male partner

With 25 years of trial and patient experience, GONAL-f® is the #1 most prescribed r-hFSH in the U.S.2 It has helped bring over 6 million babies to life worldwide.3†
Easy to teach, easy to use4
A study of 60 participants evaluated the pen injector after receiving training. Of the participants, 23 were patients (women with infertility) and rated the injector pen for ease of learning to use and ease of use (1 = difficult and 7 = easy). For ease of learning to use, approximately 20% of patients rated a 5, 65% rated a 6, and 15% rated a 7. For ease of use, approximately 5% of patients rated a 5, 70% rated a 6, and 25% rated a 7.
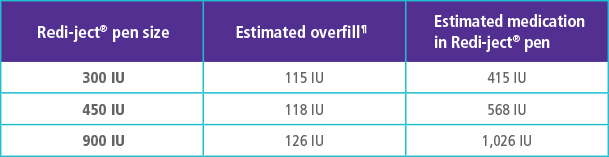
OVERFILL INFORMATION FOR GONAL-f® RFF* REDI-JECT® PENS||
Each GONAL-f® RFF* Redi-ject® pen is overfilled with approximately 115-126 International Units (IU) of medication to permit the withdrawal and administration of the labeled volumes. The chart to the right outlines the approximate amount of medication available in each Redi-ject® pen.
For ovulation induction, the maximum, individualized, daily dose of GONAL-f® RFF* Redi-ject® is 300 IU per day. For assisted reproductive technology, doses greater than 450 IU per day are not recommended.
In order to minimize the hazards associated with abnormal ovarian enlargement that may occur with GONAL-f® RFF* Redi-ject® therapy, treatment should be individualized and the lowest effective dose should be used.
‡Patients should always consult with an HCP before initiating treatment.
§Doses less than 37.5 IU have not been clinically studied and are not recommended.
||Overfill information is intended to describe the amount of medication in each Redi-ject® pen, and patients should always adhere to the dosing regimen prescribed by their doctor.
¶The actual amount of overfill in each Redi-ject® pen may vary.
Committed to smaller footprints
Sometimes less is more—which is why EMD Serono is reducing our packaging footprint with the introduction of GONAL-f® Slim Pack, a new 40% smaller pack for all GONAL-f® RFF* Redi-ject® pens.#
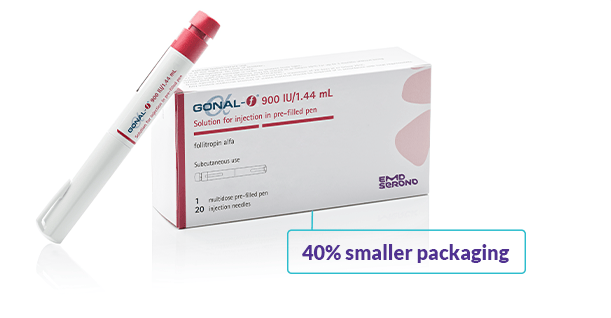
Features of the Slim Pack:
- Takes up less refrigerated space in clinics and homes
- Enables more efficient transportation and handling
- Is more discrete and portable for patients
- Makes our packaging 100% recyclable
- Will lower our global carbon footprint by 33%#
#Data on file. Audited by KPMG on Nov 2021; CO2 and plastic savings reflect annual estimates at the time of full global Slim Pack implementation. Calculations are based on comparison of most recent calendar year of global pen shipments vs. the equivalent if shipping the new Slim Pack, considering the reduction of the packaging box from 96 x 45 x 215.5 mm to 77.5 x 42 x 157 mm. This results in a 40% volume reduction, that will allow fitting an increased number of units per pallet with the new packaging solution. Carbon footprint defined as the CO2 emissions due to transportation of pen products between Merck, KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany manufacturing sites and primary destination / port of entry in each country. Plastic savings calculated using the unit weight of individual plastic tray and multiplied by the total production volume in one calendar year, once Slim Pack fully implemented across all fertility pens worldwide.
Clinical trial efficacy in OI and ART1
Ovulation induction (OI)
Study design
Ovulation induction was evaluated in a randomized, assessor-blind, multinational, multicenter, active-controlled, study in oligo-anovulatory infertile women. Women were randomized to either GONAL-f® RFF* Redi-ject® (n=83), administered subcutaneously, or a comparator r-hFSH. The use of insulin-sensitizing agents was allowed during the study. The study was designed to evaluate and compare mean ovulation rates in the first cycle of treatment. Results for GONAL-f® RFF* Redi-ject® are presented in below. Also presented in this table are secondary outcome results from cycle 1 through cycle 3. The study was not powered to demonstrate differences in any of the secondary outcomes.
Results with GONAL-f® RFF* Redi-ject®
Cycle |
Cumulativea Percent Ovulation |
Cumulativea Clinical Pregnancyd Rate |
Cycle 1 |
72%b |
28%c |
Cycle 2 |
89%c |
41%c |
Cycle 3 |
92%c |
45%c |
aCumulative rates were determined per woman over cycles 1, 2, and 3.
bNoninferior to comparator r-hFSH based on a two-sided 95% confidence interval, intent-to-treat analysis.
cSecondary efficacy outcomes. The study was not powered to demonstrate differences in these outcomes.
dClinical pregnancy was defined as a pregnancy for which a fetal sac (with or without heart activity) was visualized by ultrasound on day 34-36 after Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) administration.
The following common adverse reactions were reported at ≥2% in OI clinical trials.
System Organ Class/ |
GONAL-f® RFF* Redi-ject® N=83a (176 treatment cyclesb) nc (%) |
Central and peripheral nervous system |
|
Headache |
22 (26.5%) |
Gastrointestinal system |
|
Abdominal pain |
10 (12.0%) |
Nausea |
3 (3.6%) |
Flatulence |
3 (3.6%) |
Diarrhea |
3 (3.6%) |
Neoplasm |
|
Ovarian cyst |
3 (3.6%) |
Reproductive, female |
|
Ovarian hyperstimulation |
6 (7.2%) |
Application site |
|
Injection site pain |
4 (4.8%) |
Injection site inflammation |
2 (2.4%) |
a Total number of women treated with GONAL-f® RFF* Redi-ject®.
b Up to 3 treatment cycles per woman.
c Number of women with the adverse reaction.
Assisted reproductive technology (ART)
Study design
The efficacy of GONAL-f® RFF* Redi-ject® was evaluated in a randomized, assessor-blind, multinational, multicenter, active controlled study in healthy normal ovulatory, infertile women treated for one cycle with controlled ovarian stimulation, as part of an ART [in vitro fertilization (IVF), or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)] cycle. Women were randomized to either GONAL-f® RFF* Redi-ject® 16 (n=237), administered subcutaneously, or a comparator r-hFSH. Randomization was stratified by insemination technique, (IVF vs. ICSI). All women received pituitary down-regulation with a GnRH agonist before stimulation with r-hFSH. Efficacy was assessed using the mean number of fertilized oocytes the day after insemination. The initial doses of GONAL-f® RFF* Redi-ject® were 150 International Units per day for women less than 35 years of age and 225 International Units per day for women 35 years of age and older. The maximum dose given for both age groups was 450 International Units per day. Treatment outcomes for GONAL-f® RFF* Redi-ject® are summarized in the table below.
Results with GONAL-f® RFF* Redi-ject®
Study Outcome |
Value (n) |
Mean number of 2PN oocytes per woman |
6.3 (237)a |
Mean number of 2PN oocytes per subject receiving IVF |
6.1 (n=88)b |
Mean number of 2PN oocytes per subject receiving ICSI |
6.5 (n=132)b |
Clinical pregnancyc rate per attempt |
33.5% (n=218)d |
Clinical pregnancyc rate per embryo transfer |
35.8% (n=204)d |
Mean treatment duration in days (range) |
9.7 [3-21] (n=230)d |
aNoninferior to comparator r-hFSH based on a two-sided 95% confidence interval, intent-to-treat analysis.
bSubgroup analyses. The study was not powered to demonstrate differences in subgroups.
cA clinical pregnancy was defined as a pregnancy during which a fetal sac (with or without heart activity) was visualized by ultrasound on day 35-42 after hCG administration.
dSecondary efficacy outcomes. The study was not powered to demonstrate differences in these outcomes.
The following common adverse reactions were reported at ≥2% in ART clinical trials.
| System Organ Class/ Adverse Reactions |
GONAL-F® RFF* Redi-ject® N=237anb (%) |
|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal system | |
| Abdominal pain | 55 (23.2%) |
| Nausea | 19 (8.0%) |
| Body as a whole-general | |
| Abdomen enlarged | 33 (13.9%) |
| Central and peripheral nervous system | |
| Headache | 44 (18.6%) |
| Application site disorders | |
| Injection site bruising | 23 (9.7%) |
| Injection site pain | 13 (5.5%) |
| Injection site inflammation | 10 (4.2%) |
| Injection site reaction | 10 (4.2%) |
| Application site edema | 6 (2.5%) |
| Reproductive, female | |
| Ovarian hyperstimulation | 11 (4.6%) |
a Total number of women treated with GONAL-f® RFF* Redi-ject®.
b Number of women with the adverse reaction.
All images may be resized to scale for illustrative purposes only.
r-hFSH = recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone; IVF = in vitro fertilization; ICSI = intracytoplasmic sperm injection.
*RFF = revised formulation female.
†The original GONAL-f formulation was approved for use in Europe in 1995.
References
1. GONAL-f® RFF Redi-ject® [Prescribing Information]. EMD Serono, Inc.; 2025.
2. Data on file. IQVIA Market Data Analysis. January 2024.
3. Borget I, et al. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2024;1-15.
4. Mahony M, et al. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2018;15(1):5-15.
IMPORTANT RISK INFORMATION & INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Important Risk Information for Gonal-f® RFF* Redi-ject® (follitropin alfa injection)
Indications and Usage:
- Induction of ovulation (OI) and pregnancy in oligo-anovulatory women in whom the cause of infertility is functional and not due to primary ovarian failure
- Development of multiple follicles in ovulatory women as part of an Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) cycle.
Prior to treatment complete an evaluation of female and male partners to determine infertility diagnosis and fertility status. Primary ovarian failure and pregnancy should be excluded.
Contraindications:
- prior hypersensitivity to r-hFSH preparations or excipients
- high levels of FSH indicating primary gonadal failure
- pregnancy – apprise women of the potential hazard to the fetus if administered during pregnancy
- uncontrolled non-gonadal endocrinopathies (thyroid, adrenal, pituitary disorders)
- sex hormone dependent tumors of the reproductive tract and accessory organs
- tumors of pituitary gland or hypothalamus
- abnormal uterine bleeding of undetermined origin
- ovarian cyst or enlargement of undetermined origin, not due to polycystic ovary syndrome.
Warnings and Precautions:
- For use by physicians specializing in fertility treatment or reproductive health and only when appropriate monitoring facilities are available. Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® contains a gonadotropic substance capable of causing Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) in women with or without pulmonary or vascular complications. Careful selection should be given to the diagnosis of infertility and the selection so candidates for therapy. The lowest effective dose should be used.
- Hypersensitivity Reactions and Anaphylaxis: Serious systemic hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported in post-marketing experience. Symptoms have included dyspnea, facial edema, pruritis, and urticaria. If an anaphylactic or other serious allergic reaction occurs, initiate appropriate therapy including supportive measures if cardiovascular instability and/or respiratory compromise occur, and discontinue further use.
- Abnormal Ovarian Enlargement: Treatment should be individualized, and the lowest effective dose should be used. Use of ultrasound monitoring of ovarian response and/or measurement of serum estradiol levels is important to minimize the risk of ovarian stimulation. If the ovaries are enlarged on the last day of therapy, hCG should not be administered to reduce the risk of developing OHSS. Prohibit intercourse in women with significant ovarian enlargement.
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS): OHSS occurs after gonadotropin treatment discontinuation and can develop rapidly. If there is evidence that OHSS may be developing prior to hCG administration, hCG must be withheld. If serious OHSS occurs, gonadotropins, including hCG, should be stopped and consider if hospitalization is needed.
- Pulmonary and Vascular Complications: Serious pulmonary complications (e.g., atelectasis, acute respiratory distress syndrome and exacerbation of asthma) have been reported in women treated with gonadotropins. Thromboembolic events both in association with and separate from OHSS have been reported in women treated with gonadotropins including Gonal-f® RFF*. Women with generally recognized risk factors for thrombosis, such as personal or family history, severe obesity, or thrombophilia, may have an increased risk of venous or arterial thromboembolic events, during or following treatment with gonadotropins. Sequelae of such reactions have included venous thrombophlebitis, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary infarction, cerebral vascular occlusion (stroke), and arterial occlusion resulting in loss of limb and rarely in myocardial infarctions. In rare cases, pulmonary complications and/or thromboembolic reactions have resulted in death. In women with recognized risk factors, the benefits of OI and ART need to be weighed against the risks.
- Ovarian torsion: has been reported after treatment with gonadotropins. This may be related to OHSS, pregnancy, previous abdominal surgery, past history of ovarian torsion, previous or current ovarian cyst and polycystic ovaries. Damage to the ovary due to reduced blood supply can be limited by early diagnosis and immediate detorsion.
- Multi-fetal Gestation and Birth: During clinical trials, multiple births occurred in 20% of live births in women receiving therapy for ovulation induction and 35.1 % of live births in women undergoing ART. The woman and her partner should be advised of the potential risk of multi-fetal gestation and birth before beginning therapy with Gonal-f® RFF* Redi-ject®.
- Congenital Malformations: The incidence of congenital malformations after some ART [specifically in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)] may be slightly higher than after spontaneous conception. This slightly higher incidence is thought to be related to differences in parental characteristics (e.g., maternal age, maternal and paternal genetic background, sperm characteristics) and to the higher incidence of multi-fetal gestations after IVF or ICSI.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Since women undergoing ART often have tubal abnormalities, the incidence of ectopic pregnancy may be increased.
- Spontaneous Abortion: The incidence of spontaneous abortion (miscarriage) may be increased. However, causality has not been established. This may be a factor of the underlying infertility.
- Ovarian Neoplasms: Both benign and malignant ovarian neoplasms have been infrequently reported in women who have had multiple drug therapy for controlled ovarian stimulation; causality has not been established.
- Laboratory Tests: Both ultrasound and serum estradiol measurement should be used to monitor follicular growth and maturation, timing of the ovulatory trigger, detecting ovarian enlargement, and minimizing the risk of the OHSS and multiple gestation.
Adverse Reactions:
The most common adverse reactions (≥5%) in OI include: headache, abdominal pain, and ovarian hyperstimulation. The most common adverse reactions (≥5%) in ART include: abdominal pain, nausea, abdominal enlargement, headache, and injection site reactions (pain, bruising).
Patient Counseling:
In addition to advising patients about the proper use of treatment, the duration and necessity of monitoring, handling of missed doses, OHSS, and multi-fetal gestation and birth, patients should be advised to review the Patient Information Leaflet which contains risk information, follow the Instructions for Use for the Gonal-f® RFF* Redi-ject®, not share the device or reuse needles, and to ask their Healthcare Provider about questions.
![]() For more information, please see the full Prescribing Information and Instructions for Use for Gonal-f® RFF* Redi-ject®
For more information, please see the full Prescribing Information and Instructions for Use for Gonal-f® RFF* Redi-ject®
* RFF = Revised Formulation Female
IMPORTANT RISK INFORMATION & INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Important Risk Information for Gonal-f® RFF* Redi-ject® (follitropin alfa injection)
Indications and Usage:
- Induction of ovulation (OI) and pregnancy in oligo-anovulatory women in whom the cause of infertility is functional and not due to primary ovarian failure
- Development of multiple follicles in ovulatory women as part of an Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) cycle.
Prior to treatment complete an evaluation of female and male partners to determine infertility diagnosis and fertility status. Primary ovarian failure and pregnancy should be excluded.
Contraindications:
- prior hypersensitivity to r-hFSH preparations or excipients
- high levels of FSH indicating primary gonadal failure
- pregnancy – apprise women of the potential hazard to the fetus if administered during pregnancy
- uncontrolled non-gonadal endocrinopathies (thyroid, adrenal, pituitary disorders)
- sex hormone dependent tumors of the reproductive tract and accessory organs
- tumors of pituitary gland or hypothalamus
- abnormal uterine bleeding of undetermined origin
- ovarian cyst or enlargement of undetermined origin, not due to polycystic ovary syndrome.
Warnings and Precautions:
- For use by physicians specializing in fertility treatment or reproductive health and only when appropriate monitoring facilities are available. Gonal-f® RFF Redi-ject® contains a gonadotropic substance capable of causing Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) in women with or without pulmonary or vascular complications. Careful selection should be given to the diagnosis of infertility and the selection so candidates for therapy. The lowest effective dose should be used.
- Hypersensitivity Reactions and Anaphylaxis: Serious systemic hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported in post-marketing experience. Symptoms have included dyspnea, facial edema, pruritis, and urticaria. If an anaphylactic or other serious allergic reaction occurs, initiate appropriate therapy including supportive measures if cardiovascular instability and/or respiratory compromise occur, and discontinue further use.
- Abnormal Ovarian Enlargement: Treatment should be individualized, and the lowest effective dose should be used. Use of ultrasound monitoring of ovarian response and/or measurement of serum estradiol levels is important to minimize the risk of ovarian stimulation. If the ovaries are enlarged on the last day of therapy, hCG should not be administered to reduce the risk of developing OHSS. Prohibit intercourse in women with significant ovarian enlargement.
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS): OHSS occurs after gonadotropin treatment discontinuation and can develop rapidly. If there is evidence that OHSS may be developing prior to hCG administration, hCG must be withheld. If serious OHSS occurs, gonadotropins, including hCG, should be stopped and consider if hospitalization is needed.
- Pulmonary and Vascular Complications: Serious pulmonary complications (e.g., atelectasis, acute respiratory distress syndrome and exacerbation of asthma) have been reported in women treated with gonadotropins. Thromboembolic events both in association with and separate from OHSS have been reported in women treated with gonadotropins including Gonal-f® RFF*. Women with generally recognized risk factors for thrombosis, such as personal or family history, severe obesity, or thrombophilia, may have an increased risk of venous or arterial thromboembolic events, during or following treatment with gonadotropins. Sequelae of such reactions have included venous thrombophlebitis, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary infarction, cerebral vascular occlusion (stroke), and arterial occlusion resulting in loss of limb and rarely in myocardial infarctions. In rare cases, pulmonary complications and/or thromboembolic reactions have resulted in death. In women with recognized risk factors, the benefits of OI and ART need to be weighed against the risks.
- Ovarian torsion: has been reported after treatment with gonadotropins. This may be related to OHSS, pregnancy, previous abdominal surgery, past history of ovarian torsion, previous or current ovarian cyst and polycystic ovaries. Damage to the ovary due to reduced blood supply can be limited by early diagnosis and immediate detorsion.
- Multi-fetal Gestation and Birth: During clinical trials, multiple births occurred in 20% of live births in women receiving therapy for ovulation induction and 35.1 % of live births in women undergoing ART. The woman and her partner should be advised of the potential risk of multi-fetal gestation and birth before beginning therapy with Gonal-f® RFF* Redi-ject®.
- Congenital Malformations: The incidence of congenital malformations after some ART [specifically in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)] may be slightly higher than after spontaneous conception. This slightly higher incidence is thought to be related to differences in parental characteristics (e.g., maternal age, maternal and paternal genetic background, sperm characteristics) and to the higher incidence of multi-fetal gestations after IVF or ICSI.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Since women undergoing ART often have tubal abnormalities, the incidence of ectopic pregnancy may be increased.
- Spontaneous Abortion: The incidence of spontaneous abortion (miscarriage) may be increased. However, causality has not been established. This may be a factor of the underlying infertility.
- Ovarian Neoplasms: Both benign and malignant ovarian neoplasms have been infrequently reported in women who have had multiple drug therapy for controlled ovarian stimulation; causality has not been established.
- Laboratory Tests: Both ultrasound and serum estradiol measurement should be used to monitor follicular growth and maturation, timing of the ovulatory trigger, detecting ovarian enlargement, and minimizing the risk of the OHSS and multiple gestation.
Adverse Reactions:
The most common adverse reactions (≥5%) in OI include: headache, abdominal pain, and ovarian hyperstimulation. The most common adverse reactions (≥5%) in ART include: abdominal pain, nausea, abdominal enlargement, headache, and injection site reactions (pain, bruising).
Patient Counseling:
In addition to advising patients about the proper use of treatment, the duration and necessity of monitoring, handling of missed doses, OHSS, and multi-fetal gestation and birth, patients should be advised to review the Patient Information Leaflet which contains risk information, follow the Instructions for Use for the Gonal-f® RFF* Redi-ject®, not share the device or reuse needles, and to ask their Healthcare Provider about questions.
![]() For more information, please see the full Prescribing Information and Instructions for Use for Gonal-f® RFF* Redi-ject®
For more information, please see the full Prescribing Information and Instructions for Use for Gonal-f® RFF* Redi-ject®
* RFF = Revised Formulation Female