A flexible approach to dosing1
GONAL-f® Multi-Dose is indicated for:
- Induction of ovulation (OI) and pregnancy in oligo-anovulatory infertile women for whom the cause of infertility is functional and not due to primary ovarian failure
- Development of multiple follicles in ovulatory infertile women as part of an Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) cycle
- Induction of spermatogenesis in infertile men with primary and secondary hypogonadotropic hypogonadism for whom the cause of infertility is not due to primary testicular failure
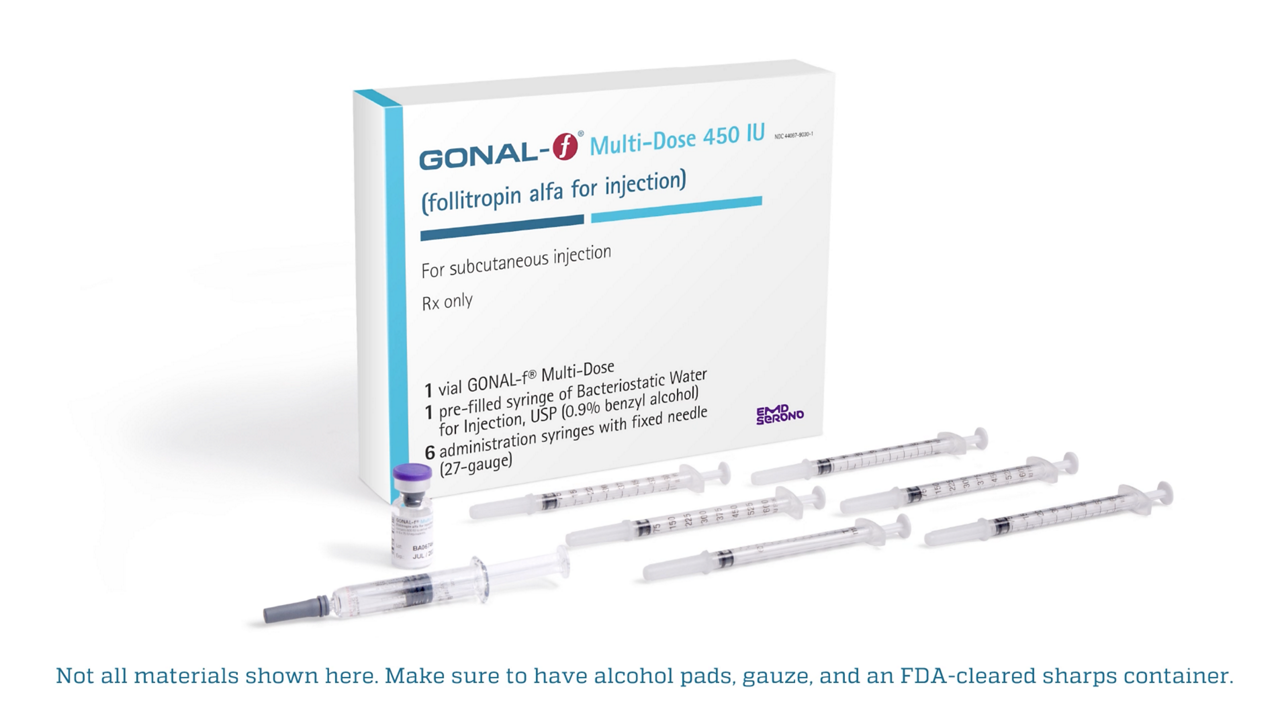

With 25 years of trial and patient experience, GONAL-f is the #1 most prescribed r-hFSH in the U.S.2 It has helped bring over 6 million babies to life worldwide.3†

GONAL-f Multi-Dose is appropriate for patients who require precise dosing, for more individualized control
Injection syringes provide half-dose increments, allowing for doses of 37.5 IU up to 75 IU
Ovulation Induction
- Initial starting dose of the first cycle - 75 International Units of GONAL-f RFF* Multi-Dose per day for 14 days, administered subcutaneously
- Individualization doses after 14 days
- Doses larger than 300 International Units of r-hFSH per day are not recommended
Assisted Reproductive Technology
- Initial starting dose of the first cycle - 150 International Units per day, administered subcutaneously
- Dosage adjustments after 3-5 days and by 75-150 International Units at each adjustment
- Do not administer doses greater than 450 International Units per day
Clinical trial efficacy in OI and ART1
Ovulation induction (OI)
Study design
The safety and efficacy of GONAL-f Multi-Dose were examined in a randomized, open-label, multicenter, active-controlled trial conducted in the U.S in oligo-anovulatory infertile women. Women were randomized to GONAL-f Multi-Dose, administered subcutaneously, or a comparator urofollitropin product, administered intramuscularly.
The primary efficacy parameter was the ovulation rate. Two hundred and thirty-two women received treatment for up to three cycles with GONAL-f Multi-Dose (118 women) or urofollitropin (114 women).
Ovulation results for women who received treatment with GONAL-f Multi-Dose in at least one cycle are summarized in Table 5.
Results with GONAL-f Multi-Dose
Cumulativea Percent Ovulation | GONAL-f Multi-Dose (n=118) |
Cycle 1 | 58%b |
Cycle 2 | 72%c |
Cycle 3 | 81%c |
Cumulativea Clinical Pregnancyd Rate |
|
Cycle 1 | 13%c |
Cycle 2 | 25%c |
Cycle 3 | 37%c |
aCumulative rates were determined per woman over cycles 1, 2, and 3.
bNon-inferior to comparator recombinant human r-hFSH based on a two-sided 95% confidence interval, intent-to-treat analysis.
cSecondary efficacy outcomes. The trial was not powered to demonstrate differences in these outcomes.
dClinical pregnancy was defined as a pregnancy for which a fetal sac (with or without heart activity) was visualized by ultrasound on day 34-36 after hCG administration.
For the 44 women in the GONAL-f group who achieved clinical pregnancy, 22.7 % did not reach a term pregnancy, 63.6% had singleton births and 13.7% had multiple births.
In a randomized, open-labeled, multicenter, active-controlled trial in oligo-anovulatory infertile women, conducted in the U.S., a total of 118 oligo-anovulatory infertile women were randomized to and underwent ovulation induction with GONAL-F versus a comparator urofollitropin. Adverse reactions occurring in at least 5.0% of women receiving GONAL-F Multi-Dose are listed in Table 1.
System Organ Class/Adverse Reactions | GONAL-F Multi-Dose N=118a (288 treatment cyclesb) nc (%) | |
Body as a Whole - General |
| |
Pain | 6 (5.1%) | |
Central and Peripheral Nervous System |
| |
Headache | 12 (10.2%) | |
Gastrointestinal System |
| |
Abdominal Pain | 9 (7.6%) | |
Nausea | 7 (5.9%) | |
Flatulence | 7 (5.9%) | |
Reproductive, Female |
| |
Intermenstrual Bleeding | 6 (5.1%) | |
Ovarian Hyperstimulation | 8 (6.8%) | 2.6% |
Ovarian Cyst | 17 (14.4%) | 1.8% |
aTotal number of women treated with GONAL-F Multi-Dose.
bUp to 3 treatment cycles per woman.
cNumber of women with the adverse reaction.
Assisted reproductive technology (ART)
Study design
The efficacy of GONAL-f Multi-Dose in ART was evaluated in a randomized, open-label, multicenter, active-controlled trial conducted in the US, in ovulatory, infertile women undergoing stimulation of multiple follicles for In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) and Embryo Transfer (ET). All women received a gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist for pituitary down-regulation before randomization and administration of GONAL-f Multi-Dose (n=56) or a comparator urofollitropin product (n=58). The primary efficacy endpoint was the number of mature pre-ovulatory follicles on the day of hCG administration. The trial was not powered to demonstrate differences in secondary outcomes.
Treatment outcomes for a single IVF cycle with controlled stimulation with GONAL-f Multi-Dose are summarized in Table 6.
Results with GONAL-f Multi-Dose
Cumulative ovulation rate | GONAL-f Multi-Dose (n=56) |
Mean number of follicles ≥14mm in diameter on day of hCGa (n=50) | 7.2 |
Mean number of oocytes recovered per patientb (n=49) | 9.3 |
Mean Serum E2 (pg/mL) on day of hCGb (n=46) | 1221 |
Mean treatment duration in days (range)b (n=56) | 10.1 (5-15) |
Clinical pregnancya rate per attemptb (n=56) | 20% |
Clinical pregnancyc rate per embryo transferb (n=47) | 23% |
aPrimary efficacy outcome.
bSecondary efficacy outcomes. The trial was not powered to demonstrate differences in these outcomes.
cClinical pregnancy was defined as a pregnancy for which a fetal sac (with or without heart activity) was visualized by ultrasound on day 34-36 after hCG administration.
For the 11 women in the GONAL-F Multi-Dose group who achieved clinical pregnancy, 36.3% did not reach a term pregnancy, 36.3% had singleton births and 27.3% had multiple births.
Study design
An additional randomized, open-label, multinational, multicenter study in ovulatory infertile women was conducted in non-U.S. countries. Women were randomized to receive either GONAL-F Multi-Dose by subcutaneous administration (60 women) or urofollitropin by intramuscular administration (63 women) after down-regulation of the pituitary with a GnRH agonist. The primary efficacy parameter was the number of mature pre-ovulatory follicles on the day of hCG administration. Results over a single IVF cycle for the primary efficacy outcome of mature pre-ovulatory follicles on the day of hCG administration were similar to the primary efficacy results presented in Table 6 for the U.S. ART trial.
In a randomized, open-labeled, active-comparator trial conducted in the U.S., a total of 56 normal ovulatory infertile women were randomized and received GONAL-F Multi-Dose versus a urofollitropin comparator as part of an ART [in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection cycle (ICSI)] cycle. All women received pituitary down-regulation with gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist before stimulation. Adverse Reactions occurring in at least 5.0% of women are listed in Table 2.
System Organ Class/Adverse Reactions | GONAL-F Multi-Dose (N=56a) nb (%) |
Central and Peripheral Nervous System |
|
Headache | 7 (12.5%) |
Gastrointestinal system |
|
Abdominal Pain | 3 (5.4%) |
Nausea | 4 (7.1%) |
Reproductive, Female |
|
Pelvic Pain | 4 (7.1%) |
aTotal number of women treated with GONAL-F Multi-Dose.
bNumber of women with the adverse reaction.
r-hFSH = recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone.
References
1. GONAL-f® RFF Multi-Dose (follitropin alfa for injection) [Prescribing Information]. EMD Serono, Inc.; 2025.
2. Data on file. IQVIA Market Data Analysis. January 2025.
3. Borget I, et al. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2024;1-15
IMPORTANT RISK INFORMATION & INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Important Risk Information for GONAL-f® Multi-Dose (follitropin alfa for injection)
Contraindications:
GONAL-f® Multi-Dose is contraindicated in women and men who exhibit:
- Prior hypersensitivity to recombinant follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) products or one of their excipients. Reactions have included anaphylaxis.
- High levels of FSH indicating primary gonadal failure
- The presence of uncontrolled non-gonadal endocrinopathies (e.g., thyroid, adrenal, or pituitary disorders)
- Sex hormone dependent tumors of the reproductive tract and accessory organs
- Tumors of pituitary gland or hypothalamus
GONAL-f Multi-Dose is also contraindicated in women who exhibit:
- Abnormal uterine bleeding of undetermined origin
- Ovarian cyst or enlargement of undetermined origin
WARNINGS
Hypersensitivity Reactions and Anaphylaxis
In the post-marketing experience, serious systemic hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported with use of GONAL-f Multi-Dose and GONAL-f RFF. Symptoms have included dyspnea, facial edema, pruritis, and urticaria. If an anaphylactic or other serious allergic reaction occurs, initiate appropriate therapy including supportive measures if cardiovascular instability and/or respiratory compromise occur, and discontinue further use.
Overstimulation of the Ovary During FSH Therapy
If serious ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) occurs, stop gonadotropins, including GONAL-f Multi-Dose and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), and consider whether the woman needs to be hospitalized.
OHSS increases the risk of injury to the ovary. Avoid pelvic examination or intercourse, as these may cause rupture of an ovarian cyst, which may result in hemoperitoneum.
A physician experienced in the management of this syndrome, or who is experienced in the management of fluid and electrolyte imbalances should be consulted.
Pulmonary and Vascular Complications:
Serious pulmonary conditions (for example, atelectasis, acute respiratory distress syndrome and exacerbation of asthma) have been reported in women treated with gonadotropins, including GONAL-f Multi-Dose. In addition, thromboembolic events both in association with, and separate from OHSS have been reported in women treated with gonadotropins, including GONAL-f Multi-Dose. Intravascular thrombosis and embolism, which may originate in venous or arterial vessels, can result in reduced blood flow to critical organs or the extremities. Women with generally recognized risk factors for thrombosis, such as personal or family history, severe obesity, or thrombophilia, may have an increased risk of venous or arterial thromboembolic events, during or following treatment with gonadotropins. Sequelae of such reactions have included venous thrombophlebitis, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary infarction, cerebral vascular occlusion (stroke), and arterial occlusion resulting in loss of limb and rarely in myocardial infarctions. In rare cases, pulmonary complications and/or thromboembolic reactions have resulted in death. In women with recognized risk factors, the benefits of ovulation induction and Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) need to be weighed against the risks. It should be noted that pregnancy also carries an increased risk of thrombosis.
Ovarian Torsion
Ovarian torsion has been reported after treatment with gonadotropins, including GONAL-f Multi-Dose. This may be related to OHSS, pregnancy, previous abdominal surgery, past history of ovarian torsion, previous or current ovarian cyst and polycystic ovaries. Early diagnosis and immediate detorsion limit damage to the ovary due to reduced blood supply.
Abnormal Ovarian Enlargement
In order to minimize the hazards associated with abnormal ovarian enlargement that may occur with GONAL-f Multi-Dose, individualize treatment and use the lowest effective dose. Use of ultrasound monitoring of ovarian response and/or measurement of serum estradiol levels is important to minimize the risk of ovarian stimulation.
If the ovaries are abnormally enlarged on the last day of GONAL-f Multi-Dose therapy, do not administer hCG in order to reduce the chance of developing Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS). Prohibit intercourse for women with significant ovarian enlargement after ovulation because of the danger of hemoperitoneum resulting from rupture of ovarian cysts
Multi-fetal Gestation and Birth
Multi-fetal gestation and births have been reported with all gonadotropin therapy, including therapy with GONAL-F Multi-Dose.
During clinical trials with GONAL-f Multi-Dose, multiple births occurred in 20% of live births in women receiving therapy for ovulation induction and 35.1% of live births in women undergoing ART. Advise the woman and her partner of the potential risk of multi-fetal gestation and birth before beginning therapy with GONAL-f Multi-Dose.
Embryofetal toxicity
The incidence of congenital malformations after some ART [specifically in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)] may be slightly higher than after spontaneous conception. This slightly higher incidence is thought to be related to differences in parental characteristics (e.g., maternal age, maternal and paternal genetic background, sperm characteristics) and to the higher incidence of multi-fetal gestations after IVF or ICSI. There are no indications that the use of gonadotropins during IVF or ICSI is associated with an increased risk of congenital malformations.
Ectopic Pregnancy
Since infertile women undergoing ART often have tubal abnormalities, the incidence of ectopic pregnancy may be increased in women who become pregnant as a result of ART. Advise women who become pregnant following ART and have: abdominal/pelvic pain (particularly on one side); shoulder, neck or rectal pain; and nausea and vomiting to seek immediate medical attention. Confirm the presence of an intrauterine pregnancy early by β-hCG testing and transvaginal ultrasound.
Spontaneous Abortion
The risk of spontaneous abortion (miscarriage) is increased with gonadotropin products, including GONAL-f Multi-Dose. However, causality has not been established. The increased risk may be a factor of the underlying infertility.
Ovarian Neoplasms
There have been infrequent reports of ovarian neoplasms, both benign and malignant, in women who have had multiple drug therapy for controlled ovarian stimulation, however, a causal relationship has not been established.
Laboratory Tests
In most instances, treatment of women with GONAL-f Multi-Dose will result only in follicular recruitment and development. In the absence of an endogenous LH surge, hCG is given to trigger ovulation when monitoring of the woman indicates that sufficient follicular development has occurred. This may be estimated by ultrasound alone or in combination with measurement of serum estradiol levels. The combination of both ultrasound and serum estradiol measurement are useful for monitoring follicular growth and maturation, timing of the ovulatory trigger, detecting ovarian enlargement and minimizing the risk of the OHSS and multiple gestation.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Women - Adverse events occurring in more than 5% of women were ovarian cyst, headache, abdominal pain, ovarian hyperstimulation, nausea, flatulence, and intermenstrual bleeding in the U.S. ovulation induction trial. In the U.S. ART trial, adverse event occurring in more than 5% of women were headache, nausea, pelvic pain and abdominal pain.
Men - There was one serious adverse reaction of gynecomastia requiring surgical excision of breast tissue in a 50-year-old man who received 9 months of therapy with GONAL-f Multi-Dose. Pathology report showed gynecomastia with no atypia. Adverse reactions reported in ≥ 2 patients were acne, injection site pain, gynecomastia, seborrhea, fatigue and libido decreased.
Specific Populations:
Pregnancy: GONAL-f Multi-Dose is not indicated in pregnant women. There is no human data that the use of gonadotropins (including GONAL-f Multi-Dose) alone or as part of IVF or ICSI cycles, increases the risk of congenital malformations.
Lactation: There are no data on the presence of GONAL-f Multi-Dose in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Because the secretion of prolactin during lactation can result in inadequate response to ovarian stimulation, advise women not to breast feed during treatment with GONAL-f Multi-Dose.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential: Because GONAL-f Multi-Dose is not indicated in pregnant women, verify a negative pregnancy test before administering GONAL-f Multi-Dose to a woman
Pediatric Use: Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use: Safety and effectiveness of GONAL-f Multi-Dose in postmenopausal women have not been established and it is not indicated in this population.
Patient Counseling:
Instruct women and men on the correct usage and dosing of GONAL-f Multi-Dose. Caution against changing the dosage or the schedule of administration unless instructed to do so by a healthcare provider.
Prior to beginning therapy with GONAL-f Multi-Dose, inform women and men about the time commitment and monitoring procedures necessary for treatment
Inform women and men that if they miss or forget to take a dose of GONAL-f Multi-Dose, they should not double the next dose and should call their healthcare provider for further dosing instructions.
For more information, please see the full Prescribing Information and Instructions for Use for GONAL-f Multi-Dose
Indications and Usage:
- Induction of ovulation (OI) and pregnancy in oligo-anovulatory infertile women for whom the cause of infertility is functional and not due to primary ovarian failure
- Development of multiple follicles in ovulatory infertile women as part of an Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) cycle
- Induction of spermatogenesis in infertile men with primary and secondary hypogonadotropic hypogonadism for whom the cause of infertility is not due to primary testicular failure
IMPORTANT RISK INFORMATION & INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Important Risk Information for GONAL-f® Multi-Dose (follitropin alfa for injection)
Contraindications:
GONAL-f® Multi-Dose is contraindicated in women and men who exhibit:
- Prior hypersensitivity to recombinant follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) products or one of their excipients. Reactions have included anaphylaxis.
- High levels of FSH indicating primary gonadal failure
- The presence of uncontrolled non-gonadal endocrinopathies (e.g., thyroid, adrenal, or pituitary disorders)
- Sex hormone dependent tumors of the reproductive tract and accessory organs
- Tumors of pituitary gland or hypothalamus
GONAL-f Multi-Dose is also contraindicated in women who exhibit:
- Abnormal uterine bleeding of undetermined origin
- Ovarian cyst or enlargement of undetermined origin
WARNINGS
Hypersensitivity Reactions and Anaphylaxis
In the post-marketing experience, serious systemic hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported with use of GONAL-f Multi-Dose and GONAL-f RFF. Symptoms have included dyspnea, facial edema, pruritis, and urticaria. If an anaphylactic or other serious allergic reaction occurs, initiate appropriate therapy including supportive measures if cardiovascular instability and/or respiratory compromise occur, and discontinue further use.
Overstimulation of the Ovary During FSH Therapy
If serious ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS) occurs, stop gonadotropins, including GONAL-f Multi-Dose and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), and consider whether the woman needs to be hospitalized.
OHSS increases the risk of injury to the ovary. Avoid pelvic examination or intercourse, as these may cause rupture of an ovarian cyst, which may result in hemoperitoneum.
A physician experienced in the management of this syndrome, or who is experienced in the management of fluid and electrolyte imbalances should be consulted.
Pulmonary and Vascular Complications:
Serious pulmonary conditions (for example, atelectasis, acute respiratory distress syndrome and exacerbation of asthma) have been reported in women treated with gonadotropins, including GONAL-f Multi-Dose. In addition, thromboembolic events both in association with, and separate from OHSS have been reported in women treated with gonadotropins, including GONAL-f Multi-Dose. Intravascular thrombosis and embolism, which may originate in venous or arterial vessels, can result in reduced blood flow to critical organs or the extremities. Women with generally recognized risk factors for thrombosis, such as personal or family history, severe obesity, or thrombophilia, may have an increased risk of venous or arterial thromboembolic events, during or following treatment with gonadotropins. Sequelae of such reactions have included venous thrombophlebitis, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary infarction, cerebral vascular occlusion (stroke), and arterial occlusion resulting in loss of limb and rarely in myocardial infarctions. In rare cases, pulmonary complications and/or thromboembolic reactions have resulted in death. In women with recognized risk factors, the benefits of ovulation induction and Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) need to be weighed against the risks. It should be noted that pregnancy also carries an increased risk of thrombosis.
Ovarian Torsion
Ovarian torsion has been reported after treatment with gonadotropins, including GONAL-f Multi-Dose. This may be related to OHSS, pregnancy, previous abdominal surgery, past history of ovarian torsion, previous or current ovarian cyst and polycystic ovaries. Early diagnosis and immediate detorsion limit damage to the ovary due to reduced blood supply.
Abnormal Ovarian Enlargement
In order to minimize the hazards associated with abnormal ovarian enlargement that may occur with GONAL-f Multi-Dose, individualize treatment and use the lowest effective dose. Use of ultrasound monitoring of ovarian response and/or measurement of serum estradiol levels is important to minimize the risk of ovarian stimulation.
If the ovaries are abnormally enlarged on the last day of GONAL-f Multi-Dose therapy, do not administer hCG in order to reduce the chance of developing Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS). Prohibit intercourse for women with significant ovarian enlargement after ovulation because of the danger of hemoperitoneum resulting from rupture of ovarian cysts
Multi-fetal Gestation and Birth
Multi-fetal gestation and births have been reported with all gonadotropin therapy, including therapy with GONAL-f Multi-Dose.
During clinical trials with GONAL-f Multi-Dose, multiple births occurred in 20% of live births in women receiving therapy for ovulation induction and 35.1% of live births in women undergoing ART. Advise the woman and her partner of the potential risk of multi-fetal gestation and birth before beginning therapy with GONAL-f Multi-Dose.
Embryofetal toxicity
The incidence of congenital malformations after some ART [specifically in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)] may be slightly higher than after spontaneous conception. This slightly higher incidence is thought to be related to differences in parental characteristics (e.g., maternal age, maternal and paternal genetic background, sperm characteristics) and to the higher incidence of multi-fetal gestations after IVF or ICSI. There are no indications that the use of gonadotropins during IVF or ICSI is associated with an increased risk of congenital malformations.
Ectopic Pregnancy
Since infertile women undergoing ART often have tubal abnormalities, the incidence of ectopic pregnancy may be increased in women who become pregnant as a result of ART. Advise women who become pregnant following ART and have: abdominal/pelvic pain (particularly on one side); shoulder, neck or rectal pain; and nausea and vomiting to seek immediate medical attention. Confirm the presence of an intrauterine pregnancy early by β-hCG testing and transvaginal ultrasound.
Spontaneous Abortion
The risk of spontaneous abortion (miscarriage) is increased with gonadotropin products, including GONAL-f Multi-Dose. However, causality has not been established. The increased risk may be a factor of the underlying infertility.
Ovarian Neoplasms
There have been infrequent reports of ovarian neoplasms, both benign and malignant, in women who have had multiple drug therapy for controlled ovarian stimulation, however, a causal relationship has not been established.
Laboratory Tests
In most instances, treatment of women with GONAL-f Multi-Dose will result only in follicular recruitment and development. In the absence of an endogenous LH surge, hCG is given to trigger ovulation when monitoring of the woman indicates that sufficient follicular development has occurred. This may be estimated by ultrasound alone or in combination with measurement of serum estradiol levels. The combination of both ultrasound and serum estradiol measurement are useful for monitoring follicular growth and maturation, timing of the ovulatory trigger, detecting ovarian enlargement and minimizing the risk of the OHSS and multiple gestation.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Women - Adverse events occurring in more than 5% of women were ovarian cyst, headache, abdominal pain, ovarian hyperstimulation, nausea, flatulence, and intermenstrual bleeding in the U.S. ovulation induction trial. In the U.S. ART trial, adverse event occurring in more than 5% of women were headache, nausea, pelvic pain and abdominal pain.
Men - There was one serious adverse reaction of gynecomastia requiring surgical excision of breast tissue in a 50-year-old man who received 9 months of therapy with GONAL-f Multi-Dose. Pathology report showed gynecomastia with no atypia. Adverse reactions reported in ≥ 2 patients were acne, injection site pain, gynecomastia, seborrhea, fatigue and libido decreased.
Specific Populations:
Pregnancy: GONAL-f Multi-Dose is not indicated in pregnant women. There is no human data that the use of gonadotropins (including GONAL-f Multi-Dose) alone or as part of IVF or ICSI cycles, increases the risk of congenital malformations.
Lactation: There are no data on the presence of GONAL-f Multi-Dose in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Because the secretion of prolactin during lactation can result in inadequate response to ovarian stimulation, advise women not to breast feed during treatment with GONAL-f Multi-Dose.
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential: Because GONAL-f Multi-Dose is not indicated in pregnant women, verify a negative pregnancy test before administering GONAL-f Multi-Dose to a woman
Pediatric Use: Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use: Safety and effectiveness of GONAL-f Multi-Dose in postmenopausal women have not been established and it is not indicated in this population.
Patient Counseling:
Instruct women and men on the correct usage and dosing of GONAL-f Multi-Dose. Caution against changing the dosage or the schedule of administration unless instructed to do so by a healthcare provider.
Prior to beginning therapy with GONAL-f Multi-Dose, inform women and men about the time commitment and monitoring procedures necessary for treatment
Inform women and men that if they miss or forget to take a dose of GONAL-f Multi-Dose, they should not double the next dose and should call their healthcare provider for further dosing instructions.
For more information, please see the full Prescribing Information and Instructions for Use for GONAL-f Multi-Dose
Indications and Usage:
- Induction of ovulation (OI) and pregnancy in oligo-anovulatory infertile women for whom the cause of infertility is functional and not due to primary ovarian failure
- Development of multiple follicles in ovulatory infertile women as part of an Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) cycle
- Induction of spermatogenesis in infertile men with primary and secondary hypogonadotropic hypogonadism for whom the cause of infertility is not due to primary testicular failure


